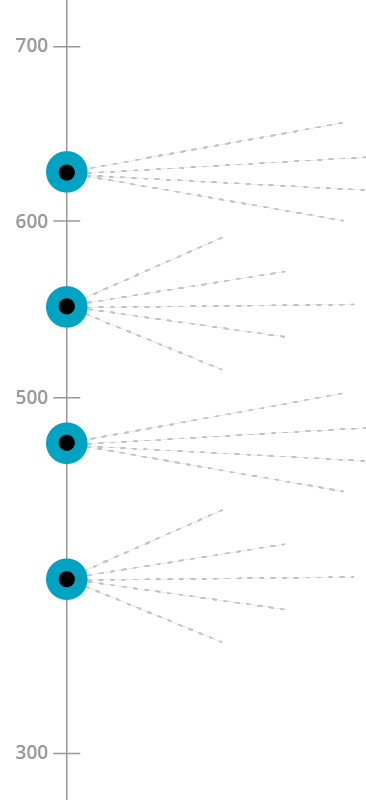
TIMSS 2015 International Benchmarks of Mathematics Achievement
As a way of interpreting the scaled achievement results, four points on the mathematics achievement scales were identified as international benchmarks—Advanced (625), High (550), Intermediate (475), and Low (400). The TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center worked with the TIMSS 2015 Science and Mathematics Item Review Committee (SMIRC) to conduct a detailed scale anchoring analysis to describe mathematics achievement at the benchmarks, and to select example items to illustrate the mathematics content and types of cognitive processing skills and strategies demonstrated by students at each of the international benchmarks. For the items designated for use in reporting the results, every effort was made to include examples that not only illustrated the particular benchmark under consideration, but also represented different item formats and content area domains.
Item Map

INTERNATIONAL BENCHMARKS
Advanced International Benchmark (625)
Advanced International Benchmark (625)
Students can apply their understanding and knowledge in a variety of relatively complex situations and explain their reasoning. They can solve a variety of multi-step word problems involving whole numbers. Students at this level show an increasing understanding of fractions and decimals. They can apply knowledge of a range of two- and three-dimensional shapes in a variety of situations. They can interpret and represent data to solve multi-step problems.
More about this benchmark
High International Benchmark (550)
High International Benchmark (550)
Students can apply their knowledge and understanding to solve problems. They can solve word problems involving operations with whole numbers, simple fractions, and two-place decimals. Students demonstrate understanding of geometric properties of shapes and of angles that are less than or greater than a right angle. Students can interpret and use data in tables and a variety of graphs to solve problems.
More about this benchmark
Intermediate International Benchmark (475)
Intermediate International Benchmark (475)
Students can apply basic mathematical knowledge in simple situations. They demonstrate an understanding of whole numbers and some understanding of fractions and decimals. Students can relate two- and three-dimensional shapes and identify and draw shapes with simple properties. They can read and interpret bar graphs and tables.
More about this benchmark
Low International Benchmark (400)
Low International Benchmark (400)
Students have some basic mathematical knowledge. They can add and subtract whole numbers, have some understanding of multiplication by one-digit numbers, and can solve simple word problems. They have some knowledge of simple fractions, geometric shapes, and measurement. Students can read and complete simple bar graphs and tables.
More about this benchmark
EXAMPLE ITEMS
ITEM 1
ITEM 2
Example Item 2
Explains why a chosen circular representation shows a given non-unit fraction
More about this item
ITEM 3
ITEM 4
ITEM 1
ITEM 2
Example Item 2
Solves a multi-step problem involving two-place decimals and whole numbers
More about this item
ITEM 3
Example Item 3
Draws a specified geometric shape by connecting dots on a circle
More about this item
ITEM 4
ITEM 5
Example Item 5
Compares information in a table and a bar graph to solve a problem
More about this item
ITEM 1
Example Item 1
Solves a two-step word problem involving subtraction and division
More about this item
ITEM 2
ITEM 3
ITEM 4
ITEM 1
ITEM 2
ITEM 3
ITEM 4
Example Item 4
Identifies the greatest volume of four rectangular prisms represented pictorially
More about this item
ITEM 5
Summary
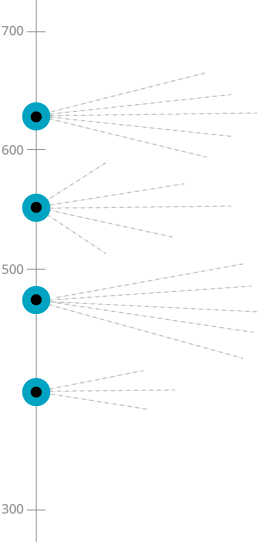
Item Map

INTERNATIONAL BENCHMARKS
Advanced International Benchmark (625)
Advanced International Benchmark (625)
Students can apply and reason in a variety of problem situations, solve linear equations, and make generalizations. They can solve a variety of fraction, proportion, and percent problems and justify their conclusions. Students can use their knowledge of geometric figures to solve a wide range of problems about area. They demonstrate understanding of the meaning of averages and can solve problems involving expected values.
More about this benchmark
High International Benchmark (550)
High International Benchmark (550)
Students can apply their understanding and knowledge in a variety of relatively complex situations. They can use information to solve problems involving different types of numbers and operations. They can relate fractions, decimals, and percentages to each other. Students at this level show basic procedural knowledge related to algebraic expressions. They can solve a variety of problems with angles including those involving triangles, parallel lines, rectangles, and similar figures. Student can interpret data in a variety of graphs and solve simple problems involving outcomes and probabilities.
More about this benchmark
Intermediate International Benchmark (475)
Intermediate International Benchmark (475)
Students can apply basic mathematical knowledge in a variety of situations. They can solve problems involving negative numbers, decimals, percentages, and proportions. Students have some knowledge of linear expressions and two- and three-dimensional shapes. They can read and interpret data in graphs and tables. They have some basic knowledge of chance.
More about this benchmark
Low International Benchmark (400)
EXAMPLE ITEMS
ITEM 1
Example Item 1
Reasons about fractional parts of a whole in a word problem and explains answer
More about this item
ITEM 2
ITEM 3
Example Item 3
Constructs and uses the solution of a linear equation to solve a word problem
More about this item
ITEM 4
Example Item 4
Uses the Pythagorean theorem in finding the perimeter of a trapezoid
More about this item
ITEM 5
ITEM 1
Example Item 1
Selects and combines information from two sources to solve a multi-step word problem
More about this item
ITEM 2
Example Item 2
Identifies the formula that represents a situation involving area
More about this item
ITEM 3
Example Item 3
Finds the value of an algebraic expression involving parentheses and negative terms
More about this item
ITEM 4
Example Item 4
Solves a problem involving angles of a triangle and parallel lines
More about this item
ITEM 5
ITEM 1
ITEM 2
ITEM 3
ITEM 4
ITEM 5
ITEM 1
ITEM 2
Example Item 2
Identifies the table that matches the information shown in a pictograph
More about this item
ITEM 3
Summary
You may also be interested in...